Gum disease, also known as periodontal disease, is a common oral health condition that affects the tissues surrounding the teeth. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gum disease, empowering you to take control of your oral health.
Gum disease is a prevalent condition that can have serious consequences if left untreated. It begins with the buildup of plaque, a sticky film of bacteria that forms on the teeth. Over time, plaque can harden into tartar, leading to inflammation and infection of the gums. Without prompt intervention, gum disease can progress to more advanced stages, potentially causing tooth loss and other complications.
Causes of Gum Disease:
Several factors can contribute to the development of gum disease, including poor oral hygiene, smoking, hormonal changes, certain medications, and underlying health conditions such as diabetes. Genetics also play a role, as some individuals may be more predisposed to gum disease than others.
Symptoms of Gum Disease:
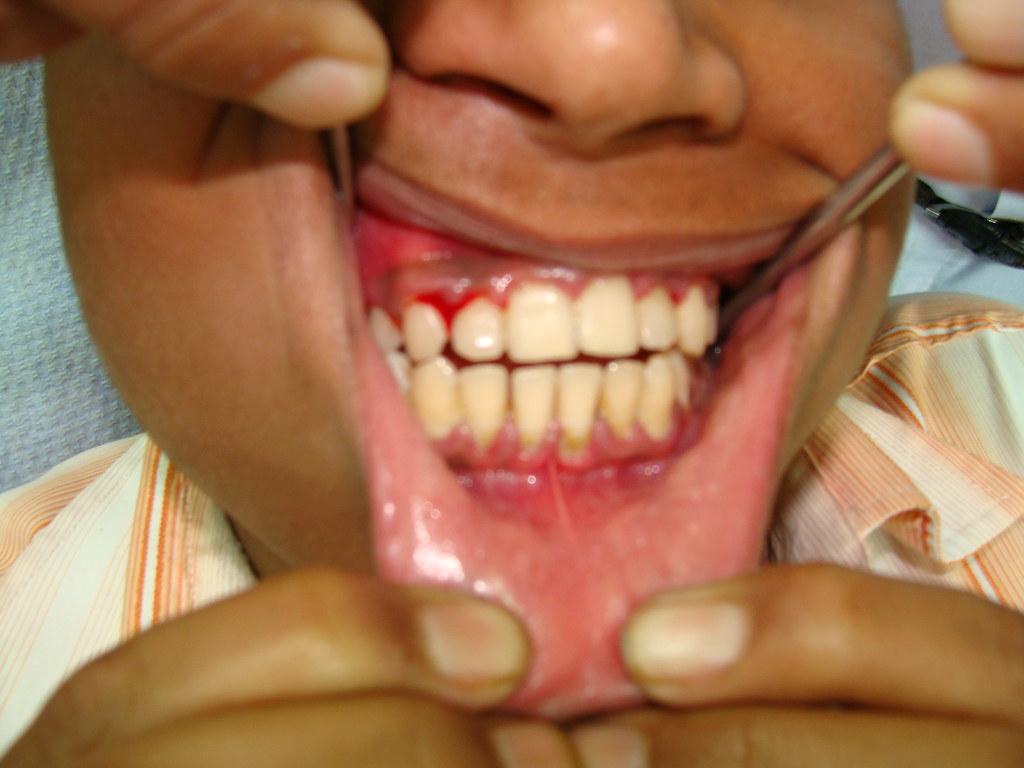
The symptoms of gum disease can vary depending on the stage of the condition. In its early stages, known as gingivitis, symptoms may include red, swollen, and bleeding gums, as well as persistent bad breath. If left untreated, gingivitis can progress to periodontitis, characterized by receding gums, loose teeth, and the formation of pockets between the teeth and gums.
Treatment Options for Gum Disease:
Fortunately, gum disease is treatable, especially when caught early. The primary goal of treatment is to control the infection, reduce inflammation, and prevent further damage to the gums and supporting structures. Common treatment options for gum disease may include:
- Professional Dental Cleaning: A thorough cleaning by a dental hygienist can remove plaque and tartar from the teeth and gums, helping to prevent the progression of gum disease.
- Scaling and Root Planing: This deep cleaning procedure involves removing plaque and tartar from below the gum line and smoothing the roots of the teeth to promote healing.
- Antibiotic Therapy: In some cases, antibiotics may be prescribed to help control bacterial infection and reduce inflammation in the gums.
- Gum Surgery: In advanced cases of gum disease, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair damaged tissues and restore gum health. Procedures such as flap surgery and tissue grafts can help regenerate lost bone and gum tissue.
- Ongoing Maintenance: After treatment, it’s essential to maintain good oral hygiene practices and attend regular dental checkups to prevent gum disease from recurring.
Conclusion:
Gum disease is a serious oral health condition that requires prompt attention and appropriate treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for gum disease, you can take proactive steps to protect your oral health and maintain a healthy smile for years to come.